Navigating Utility Billing Changes: A Look into 2024
March 19, 2024
Navigating Social Media: How to Avoid the Pitfalls of FOMO and Legal Troubles
May 29, 2024Do You Experience High Water Consumption? Learn To Fix That Today From Our COO
What is High Usage?
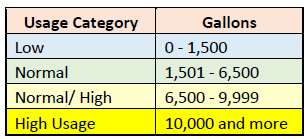
High usage indicates that a meter has measured an abnormally high volume of water or an abnormal amount for the specific resident in question. The US Government estimates that most individuals use between 2,400 and 3,000 gallons of water per month. In a multifamily home, the usage will be somewhat less at around 1,500 to 2,500 gallons per person. That means that most multifamily dwellings will consume between 1,500 to 6,500 gallons of water. Usage between 6,500 and 10,000 gallons is not necessarily abnormal, especially if there are several individuals living in the home. Usage that is over 10,000 gallons may indicate that there is an issue. This simple chart will help to identify units of concern.
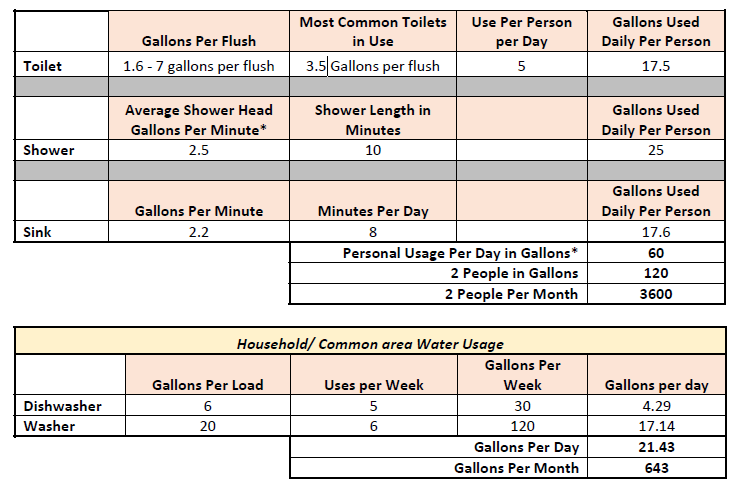
Causes of High Usage
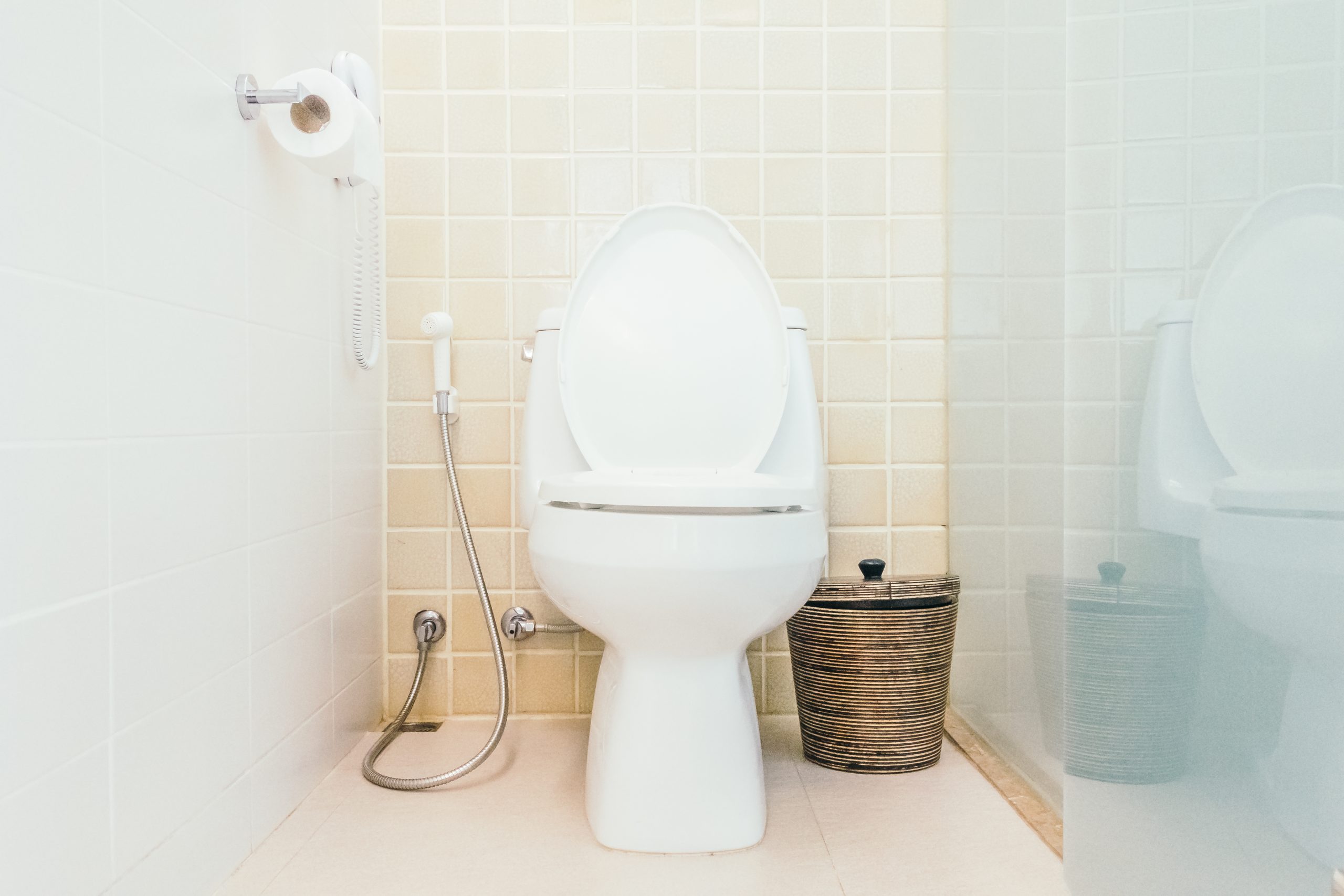
The number one source of residential high usage is the toilet. A toilet flapper is a small, circular rubber device that seals the opening between the toilet tank and bowl. It is the part that allows a toilet to flush. Toilet flappers routinely harden and warp causing water to leak from the toilet tank into the bowl, and thereby into the sewer. A toilet leak can allow thousands of gallons monthly to flow from the tank into the bowl.
Other sources of leakage include dripping faucets, showers, and hot water heater pressure relief valves. A dripping shower can waste over 300 gallons in a month. Hot water heaters have a pressure relief valve that is intended to allow them to vent if there is too much pressure. If the pressure relief valve plumbing is piped
to the outside of your home, it may be venting water without anyone’s knowledge.

Conducting a High Usage Inspection
What To Know – The number one source of unknown consumption is the toilet. It is common for a toilet flapper to warp and misalign, which causes water to flow from the tank into the bowl and down the sewer. There is often no indication that this is occurring other than the sound of the tank periodically adding water.
What You Need – toilet dye tablets or other water coloring agents. It should be noted that toilet dye tablets are ceramic-safe. Other water coloring agents may not be. Toilet dye tablets may be purchased at any hardware store.
Toilet Dye Test ‐ Put a toilet dye tablet in the tank (back) of each toilet. It will take the dye fifteen minutes to dissolve.
- Look in Each Toilet Bowl – once the Dye has been in the toilet for fifteen minutes, you will see it leaking down into the bowl if the toilet flapper is bad. You may also notice water running into the bowl. If this is the case, you have discovered the probable source of high consumption.
- Changing a Flapper – Changing a toilet flapper is a simple and easy task. There are many tutorials online that show this process. If you have never changed a toilet flapper, please type “changing a toilet flapper” into a browser search engine. Many tutorials will appear. The picture below shows an actual toilet flapper

Examine Faucets & Showers – Visually examine each fixture to see if any of them are leaking. A dripping faucet is not usually a large consumer. A leaky shower head can use much more water, up to 330 gallons per month. A badly leaking faucet will consume much more.
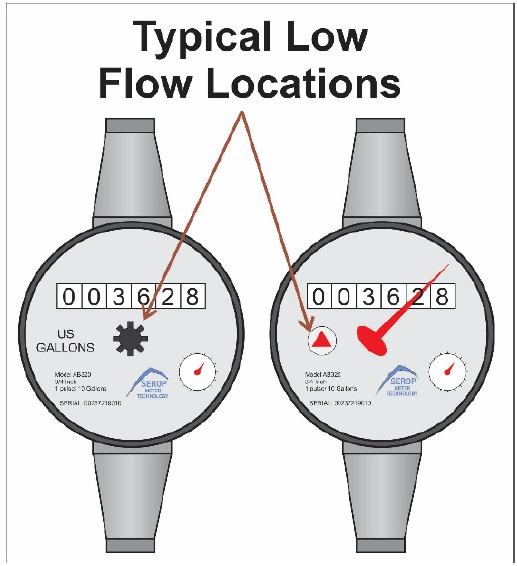
Low Flow Indicator ‐ Visually examine your water meter for signs of usage. The meter has a dial that is called a Low Flow Indicator on it. The low flow indicator will move if there is any water running through the meter. With all sources of water, usage turned off, watch the low flow indicator. Continue watching for ten minutes. If the low flow moves at all, water is passing through the meter. Here are some tips on what you might see, and what it could indicate.
- Periodic flow ‐ the low flow indicator spins every few minutes and then stops, and the pattern repeats. This is probably a toilet flapper. What you are observing is the toilet tank refilling every few minutes.
- Occasional flow ‐ If the low flow moves while you are watching, and it does not reoccur, it could be something as simple as an icemaker filling.
- Sustained flow – if the sustained flow is observed, there may be a more serious issue. This indicates that there may be a leak somewhere after the meter. If no source of water usage can be visually seen, then the water is flowing in an area that is not visible. You may need the assistance of a plumber specializing in leak detection.
The drawing below shows the low flow indicator on two different generic meters.